Supervised Learning: Fundamentals of Predictive Modeling
Image by author
Editor’s note: This article is part of a series on visualizing the basics of machine learning.
Welcome to the latest entry in our series on visualizing the basics of machine learning. This series aims to break down important and often complex technical concepts into intuitive, visual guides to help you master the core principles of the field. This entry focuses on supervised learning, the foundation of predictive modeling.
Basics of predictive modeling
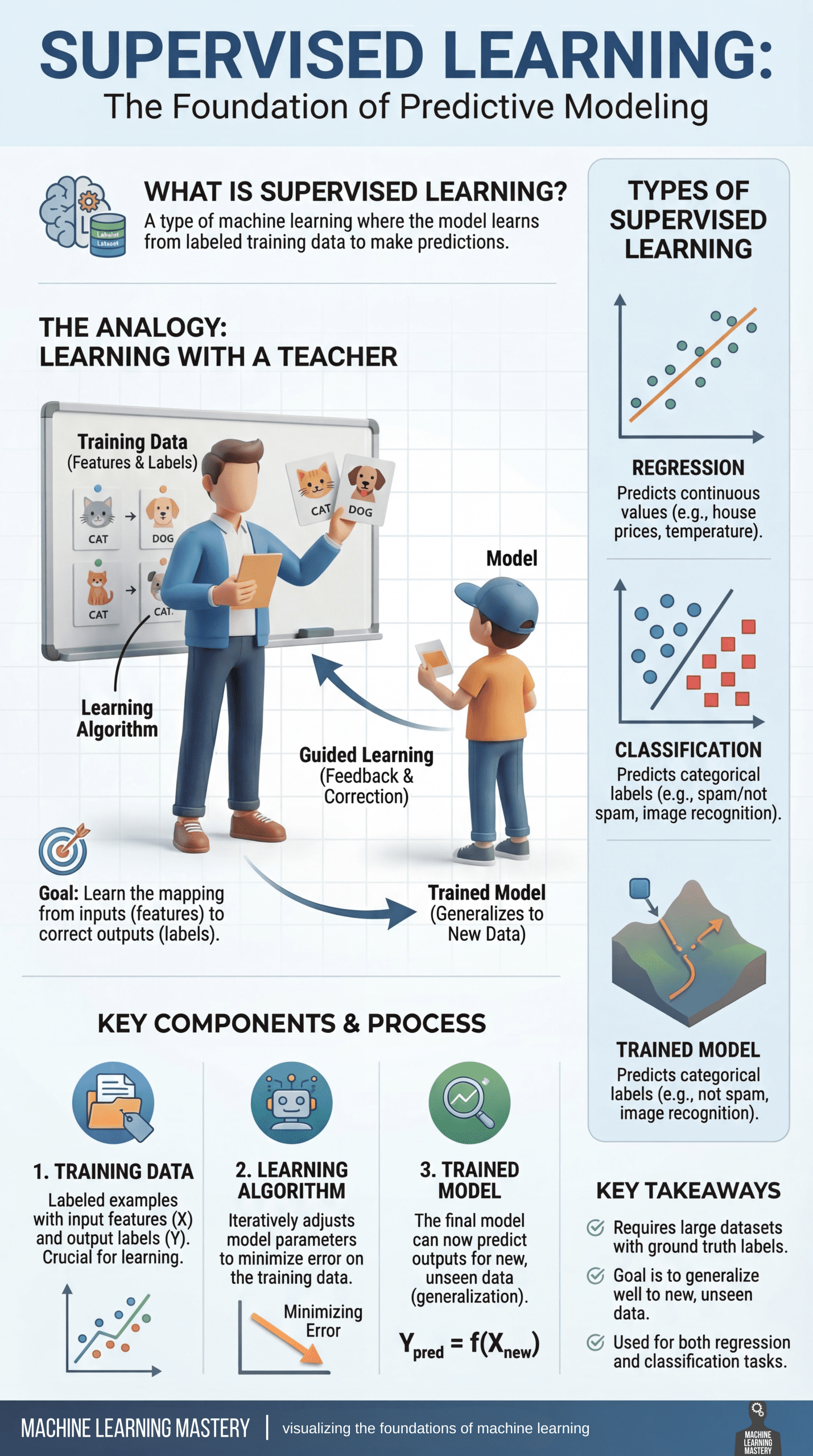
Supervised learning is widely recognized as the basis for predictive modeling in machine learning. but why?
At its core is a learning paradigm that trains models on labeled data. In the example, both the input features and the correct output (ground truth) are known. By learning from these labeled examples, the model can make accurate predictions on new and unknown data.
A helpful way to understand supervised learning is to use the following analogy. learn with teacher. During training, the model displays examples with correct answers, just as students receive guidance and correction from an instructor. Each prediction the model makes is compared to the ground truth labels, providing feedback and making adjustments to reduce future mistakes. Over time, this guided process helps the model internalize the relationships between inputs and outputs.
Purpose of supervised learning It is about learning reliable mappings from features to labels. This process revolves around three key components:
- first, training dataIt consists of labeled examples and serves as a basis for learning.
- The second is learning algorithmiteratively adjusts the model parameters to minimize the prediction error on the training data.
- lastly, trained model What emerges from this process can be generalized to predict new data.
Supervised learning problems typically fall into two main categories: regression Tasks focus on predicting continuous values, such as house prices or temperature measurements. classification On the other hand, tasks include predicting individual categories, such as distinguishing between spam and non-spam emails or recognizing objects in images. Despite their differences, Both are based on the same basic principle of learning from labeled examples..
Supervised learning plays a central role in many real-world machine learning applications. It typically requires a large, high-quality dataset with reliable ground truth labels, and its success depends on how well the trained model generalizes beyond the data used for training. When applied effectively, supervised learning allows machines to make accurate and actionable predictions across a wide range of domains.
The visualization below concisely summarizes this information for easy reference. you can Download a high-resolution PDF of the infographic here.
Supervised Learning: Visualizing Machine Learning Fundamentals (Click to Enlarge)
Image by author
Machine learning mastery resources
Below are some of the resources selected to learn more about supervised learning.
- Supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms – This entry-level article explains the differences between supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised learning, outlines how labeled and unlabeled data are used, and highlights common algorithms for each approach.
Important points: Knowing when to use labeled and unlabeled data is fundamental to choosing the appropriate learning paradigm. - Simple linear regression tutorial for machine learning – This practical, beginner-friendly tutorial introduces simple linear regression and explains how linear models are used to describe and predict the relationship between a single input variable and a numerical output.
Important points: Simple linear regression models the relationship using a straight line defined by the learned coefficients. - Linear regression for machine learning – This introductory article provides a broader overview of linear regression, explaining how the algorithm works, key assumptions, and how it can be applied in real-world machine learning workflows.
Important points: Linear regression serves as the core baseline algorithm for numerical prediction tasks. - Four types of classification tasks in machine learning – This article describes the four main types of classification problems (binary classification, multiclass classification, multilabel classification, and imbalanced classification) with clear explanations and practical examples.
Important points: Accurately identifying the type of classification problem determines model selection and evaluation strategy. - One-to-remain and one-to-one for multi-class classification – This hands-on tutorial shows how to extend binary classifiers to multiclass problems using One-vs-Rest and One-vs-One strategies, with guidance on when to use each.
Important points: Multiclass problems can be solved by decomposing them into multiple binary classification tasks.
Stay tuned for additional entries in our series on Visualizing Machine Learning Fundamentals.


